Flexbile Advanced Magnets Used for Stellarators (FAMUS)
FAMUS is a variant of FOCUS specialized for designing permanent magnets. It uses a topology optimization method to determine the presence of magnets in the entire designing space. FAMUS can optimize the magnitude and/or orientation of permanent magnet in the form of magnetic dipole subject to explicit forbidden regions and material remanence. For more details, please check Zhu, C. et al. (2020) ‘Topology optimization of permanent magnets for stellarators’, Nuclear Fusion (2020) (preprint at arXiv:2005.05504).
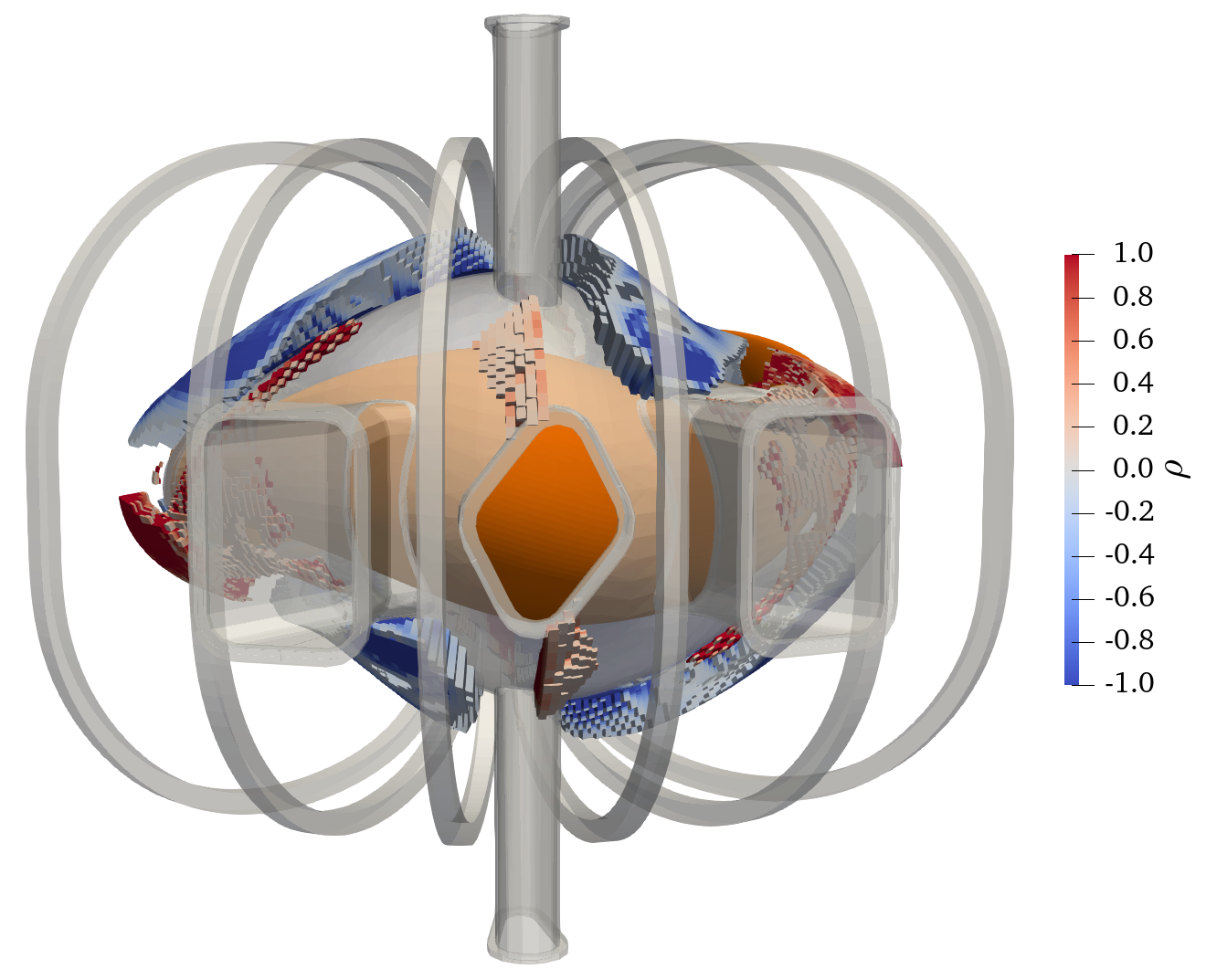
FAMUS is in the dipole branch of the FOCUS repository, although it has been modified a lot.
It shares similiar I/O with FOCUS, but there are differences.
Input files
- Input namelist
- Target plasma boundary
- Initial dipoles
Objective functions
-
Normal field error $$ F_B = \iint_{\cal S} \left ( \vec{B}_{M} \cdot \vec{n} - B_n^{tgt} \right )^2 d{a} $$
This function makes sure the prodcued magnetic field statisfies the boundary condition.
-
Total magnetic moment $$ F_M = \sum_i {m_i}^2. $$
This function will try to reduce the total amount of used magnets.
-
Binary Dipoles $$ F_D = \sum |\rho|(1 - |\rho|) , \; \mathrm{where} \; \rho = p^q \in [-1,1] $$.
This objective encourages PM cells to be either 0 or 1 instead of intermediary values.
Optimization algorithms
- Quasi-Newton (QN)
- Simulated Annealing (SA)
- Hybrid of QN & SA (HY)