BLASTOSPIM Instance Segmentation and Tracking Pipeline
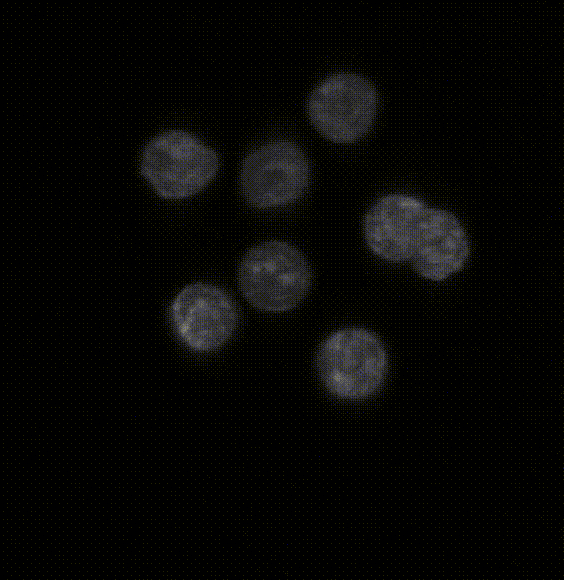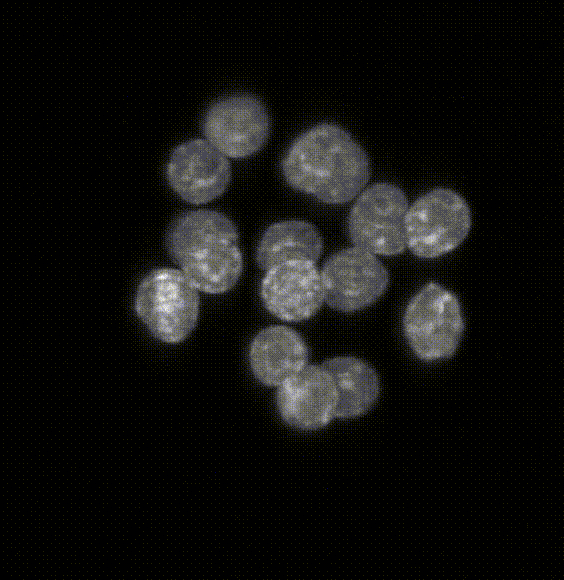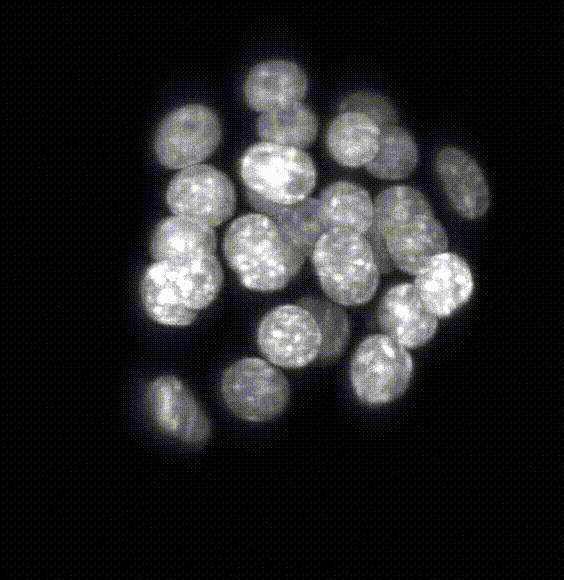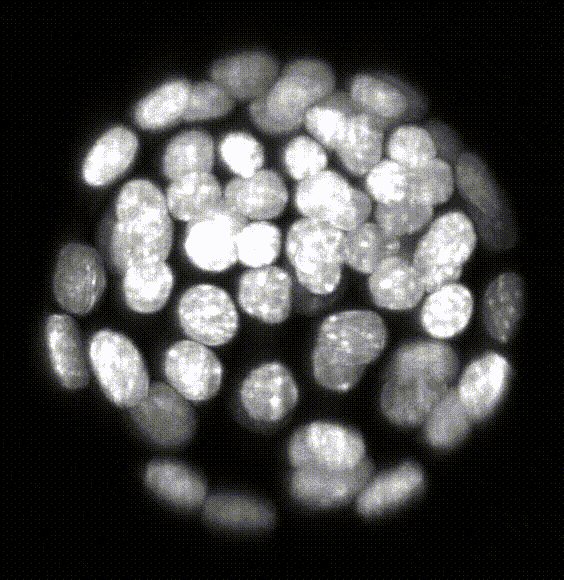
Robust 3D Nuclear Instance Segmentation of the Early Mouse Embryo
View the Project on GitHub PrincetonUniversity/blastospim-processing-pipeline
The BLASTOSPIM Instance Segmentation and Tracking Pipeline can be run by installing the software packages or by using Jupyter notebooks.
Running BLASTOSPIM with Jupyter notebooks
Follow the instructions here to use the Jupyter notebooks.
Full BLASTOSPIM Install
Follow the steps below to install of the full pipeline and run a sample dataset.
Step 1: Segmentation of Images
Install the Pipeline
You can run the following commands to install the tool in your own machine.
-
Download and install Python 3.11 version of Miniconda: https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html
-
Open “Command Prompt” and create a conda environment and activate it:
CONDA_OVERRIDE_CUDA="11.2" conda create -n tf2-segmentation python=3.9 "tensorflow==2.11.1=cuda112*" --channel conda-forge conda activate tf2-segmentation pip install "stardist_inference @ git+https://github.com/abiswas-odu/stardist_inference.git"
Download and Run Test Example
Download Example
To download the example execute the following commands:
conda activate tf2-segmentation
pip install "blastospim_download @ git+https://github.com/PrincetonUniversity/blastospim-processing-pipeline.git"
cd blastospim_download
mkdir test
cd test
blastospim-download
The commands will create a test directory and download 3 compressed folders and uncompress them in the current folder. The folders are:
- data : The data files with the following folders:
- Images : The original images from the microscope in TIF format. The images capture the transition from 8-16 cell stage division.
- Expected_Segmentation : The segmentation output that should be produced using the early stage model.
- Corrected_Segmentation : The expert corrected segmentation produced using AnnotatorJ.
- Expected_Track : The config.yaml file and the expected registration transforms and tree.
- Extract_Align : A test example that extracts intensity data from the CDX2 transcription factor channel based on the segmentation mask on the nuclear channel after appropriate alignment.
- early_embryo_model: The early model to be used for inference if the images have less than 45-50 cells.
- late_embryo_model: The late model to be used for inference if the images have greater than 45-50 cells.
Run the Instance Segmentation
stardist_inference package has a reasonable commandline interface with help.
stardist_inference --help
A sample SLURM script is provided in scripts/runInferenceSD.cmd. Change the parameters on top and use sbatch to submit.
It may be necessary to load the anaconda/miniconda module if your login does not load it to begin with.
The TIF files produced should be compared with the TIF files in Expected_Segmentation for verification.
Here is an example of the segmentation produced by the model. The left hand side of the image shows the original
image catapulted from the microscope. The right hand side is the labeled image where each pixel of a
detected object has been assigned an identifier that allows us to color the image with a look-up table in Fiji.

Step 2: Manual Correction of Labels
The manual correction of labels is performed using a ImageJ plugin tool AnnotatorJ version 1.6.
Create a Correction Directory
Create a directory with the original images and the stardist_rois directory in it.
For the test example, copy the stardist_rois generated during Step 1 into the Images folder.
Install AnnotatorJ 1.6.2
- Install JRE version 8 from here: https://www.oracle.com/in/java/technologies/javase/javase8-archive-downloads.html
- Download the AnnotatorJ 1.6.2 JAR file from here: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Tnsy-BcGLwSHmU4rwH-4taSEwHA1RqoF/view?usp=drive_link
- Change to the directory with the AnnotatorJ 1.6 JAR file and execute the command:
java -jar annotator_Project-1.6.2.jar - This should open the following 2 windows:

Performing Manual Corrections
-
Click the Open button in the AnnotatorJ 1.6.2 window and navigate to the
Imagesfolder. -
Select the image to be corrected. After the image is loaded, scroll to the frame to be corrected.

-
The boundary of the segmentation of the cells is shows in different colors. These boundaries are called Region on Interest or ROI . The
ROI Managerwindow shows the label IDs and the frame number of each cell. The same cell is colored the same across the frames of the 3D image. -
ROIs can be selected in the
ROI Managerwindow and edited. The selected ROI color changes to cyan as seen below.

- The
ROI Managerwindow and the AnnoratorJ window provide various functions to add, rename, delete individual ROIs and whole cells. These can be used to correct any segmentation errors.
Step 3: Registration of Labels and Tracking
After the labels generated by the segmentation are corrected the images need to be registered as the embryos rotate randomly.
The registration and the tracking scripts are written in MATLAB and require a config.yaml file to be created to drive the scripts.
Download the MATLAB Code
-
Download and install MATLAB.
-
Run the following commands to clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/abiswas-odu/lineage_track
Create a config.yaml file
Create a folder in your file system and create a config.yaml file which contains paths and setting for registration and tracking.
There is a sample config.yaml file in the scripts directory. Copying that as a template will make it easy.
Run the Registration
-
Open MATLAB and navigate to the
lineage_trackdirectory. -
Open the registration script
lineage_track\registration\Registration_IoU.m. -
Change the
config_pathvariable to the folder where you have yourconfig.yaml. -
Run the script. It will produce two files in the output folder
test_transforms.matandtest_transforms.json. They are the same registration transforms in MATLAB and JSON format respectively.
Visualize the Registration
On completion the registration, the registered point clouds can be viewed in sequence.
-
Open the visualization script
lineage_track\registration\VisualizeSequence.m. -
Change the
config_pathvariable to the folder where you have yourconfig.yaml. -
Run the script. It will produce 2 plots.
- A plot of the sigma of the registration for each consecutive timepoint.

- A plot of the sigma of the registration for each consecutive timepoint.
- A plot showing the point cloud representation of the registration for the first 2 time points in red and blue.
The blue circles are the point cloud representing the segmented objects at time index
tand red dots aret+1. Press enter in the MATLAB Command Window to view the next registration. All the consecutive registration can be inspected.

Tracking using the Registered Images
Once the registration transforms are known, the segmented images can be tracked to construct the lineage tree.
-
Open the tracking script
lineage_track\tree_generation\volume_track_nuclei_divisions.m. -
Change the
config_pathvariable to the folder where you have yourconfig.yaml. -
Run the script. It will produce 3 plots showing the tracking of the first two time points.
- A plot of the registered point clouds for time index
tandt+1. - A plot of a lineage tree tracked so far.
- A plot of the centroid showing the assignment of the cells from
ttot+1. Any cells that could not be tracked are shown as a triangle which need to be tracked manually by adding edges in the graph.
It pauses after tracking the cells in the next time point and the user must press enter to proceed
to the next and 3 more plots will be opened. So, it is recommended to manage the windows being opened by
closing the previous ones.

Step 4: Extracting Intensities from Tracked Images
To extract the intensity signals we use a python package that automatically aligns camera between the long short cameras used to capture the nuclear and transcription factor intensities.
- Run the following commands to clone the repository:
cd blastospim_download git clone https://github.com/abiswas-odu/Mouse_embryo_analysis_ab_fork.git - Change to the
Mouse_embryo_analysis_ab_forkdirectory and you can run the CLI help:conda activate tf2-segmentation python python tf_extract.py tf-align-simple --help - To run the sample example execute the command:
tf-align-simple --nucl_image_dir ..\test\Extract_Align\nuclei --nucl_seg_dir ..\test\Extract_Align\nuclei_seg --tf_signal_image_dir ..\test\Extract_Align\tf --crop_dir ..\test\Extract_Align\crop_dir --cropbox_index 70 --out_dir ..\test\Extract_Align\output --out_prefix align_test --timestamp_min 70 --timestamp_max 71 --align_camera_timestamps 70 --offset 150 --cell_volume_cutoff 4000 --max_margin 2048 --align_camera 1 --max_absolute_shift 50 --x_shift_override 10 --y_shift_override 10The output produced should match the result in the
Extract_Align\expected_output.