Removing the Tedium from Your Research Workflow
Linux productivity tools and practices for researchers
Suppressing Duo
Duo enhances security with the downside of being disruptive (and even annoying). This page presents two approaches to suppressing Duo while still maintaining security. Note that by “suppressing” we mean minimizing as opposed to eliminating. That is, you will still need to Duo authenticate but much less so.
The following three appproaches are described on this page:
- Use a VPN (recommended for Windows users)
- VPN-free with SSH multiplexing (recommended for Mac, Linux, and WSL users)
- VPN-free without SSH multiplexing
I. VPN Approach (recommended for Windows users)
Here is the procedure:
- Download, install, and configure the Global Protect VPN client.
- Connect via the VPN client (even if you are on-campus).
- SSH to a cluster. You will only need to Duo authenticate once per session.
To install a VPN client on your laptop/workstation follow this OIT KnowledgeBase article. GlobalProtect is recommended.
Secure Remote Access (SRA) is a service for Princeton faculty, staff, and students who are off-campus and need to access restricted campus resources through a Virtual Private Network (VPN). After authenticating, remote computers function as if they were on campus, and as long as your SRA connection is active, all Internet activity from your computer is routed through Princeton servers and your computer is giving a Princeton IP address.
OIT is responsible for the VPN so please contact them with any questions or problems.
There are two disadvantages to using the VPN: (1) it requires launching Global Protect at the start of each session and (2) the VPN has limited network performance (see below). If you would prefer not to use a VPN then see the multiplexing approach below.
What if the VPN is too slow?
The use of a VPN will decrease your internet connection speed. The table below was generated at an off-campus location in Princeton with a FIOS connection using speedtest.net:
| VPN | Download (Mbps) | Upload (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|
| None | 865 | 635 |
| None | 888 | 598 |
| GlobalProtect | 593 | 213 |
| GlobalProtect | 688 | 220 |
| SonicWall | 57 | 60 |
| SonicWall | 57 | 62 |
The SonicWall VPN severely decreases transfer rates and should be avoided. If you still find poor performance with the GlobalProtect VPN then consider the multiplexing solution described below which is VPN-free.
On campus, you can measure the speed of your network connection at https://tigerspeed.princeton.edu. If you are having trouble connecting to the Research Computing systems using SSH then see this page and in particular https://myip.rc.princeton.edu/.
Preventing VPN disconnects
If your VPN is disconnecting too frequently then try adding these lines to your ~/.ssh/config file (make the file if necessary):
Host *
Compression yes
ServerAliveInterval 30
ServerAliveCountMax 10
This will cause a “ping” every 30 seconds and hopefully prevent disconnections. OIT manages the VPN so please contact them for assistance. Consider using tmux to help deal with disconnects.
If the Linux VPN is not working
Try the procedure below from Tim Jones of the Tech Clinic if your VPN client on Linux is not working:
echo "Enter your netid"
read netid
wget --user=$netid --ask-password https://web.princeton.edu/sites/oitdownloads/vpn/Linux%20x64/ConnectTunnel-Linux64.tar
tar -xvf ConnectTunnel-Linux64.tar
sudo ./install.sh
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jre
startctui
PPPL VPN
The approach described above does not work with the PPPL Pulse Secure VPN. You will be required to Duo authenticate each time you use ssh or scp.
Host Nicknames or Abbreviations
You can connect to a cluster like Della from your local machine (e.g., laptop) using the following command:
$ ssh <YourNetID>@della.princeton.edu
However, by modifying the ~/.ssh/config file (or creating the file if necessary) on your local machine you can just do the following even if off-campus:
$ ssh della
Here is a sample ~/.ssh/config file that allows one to do this (replace aturing with your NetID):
Mac, Linux and WSL
Host adroit.princeton.edu adroit
User aturing
HostName adroit.princeton.edu
Host della.princeton.edu della
User aturing
HostName della.princeton.edu
Windows
Use a text editor to add these lines to C:\Users\<username>\.ssh:
Host adroit.princeton.edu adroit
User aturing
HostName adroit.princeton.edu
MACs hmac-sha2-512
Host della.princeton.edu della
User aturing
HostName della.princeton.edu
MACs hmac-sha2-512
The first line in each stanza above specifies alternative names for the host. Put your Princeton NetID in the second line (i.e., replace aturing). The third line in each stanza should remain unchanged. You can add additional stanzas for other clusters or machines.
(Windows) Corrupted MAC on input
If you encounter Corrupted MAC on input or ssh_dispatch_run_fatal then see this solution.
II. Multiplexing Approach (VPN free, large clusters only, recommended for Mac and Linux)
Multiplexing involves the simultaneous transmission of several messages along a single channel of communication.
To use this approach, you must have an account on one of the large clusters: Della, Stellar or Tiger
The following solution is from Bill Wichser of Research Computing.
Q: How do I avoid having to authenticate with Duo every time?
A: Yes this is painful! But there are a few things one can do. I will explain one approach using ssh multiplexing which uses a single ssh connection and sends all communication over that channel. This means that you will only need to Duo authenticate once.
But do be aware of why Duo is being used in the first place. It is to protect our systems. The reason I mention this is because you do have options with the method I am going to provide with respect to time limits on how long the multiplexed functionality remains operational. Set too low and your very next ssh/scp will require Duo authentication again. But set too high, the protection could be bypassed which makes us all vulnerable.
Note that a VPN is required from off-campus to use the OnDemand web portals of MyAdroit, MyDella, MyStellar and MyTiger as well as for various library services such as downloading journal articles.
On-Campus and Off-Campus (Recommended)
When off-campus and not using a VPN, one cannot ssh to the login node of a Research Computing cluster. However, for users with an account on one of the large clusters (not Adroit, not Nobel) one can use tigressgateway as a proxyjump server:
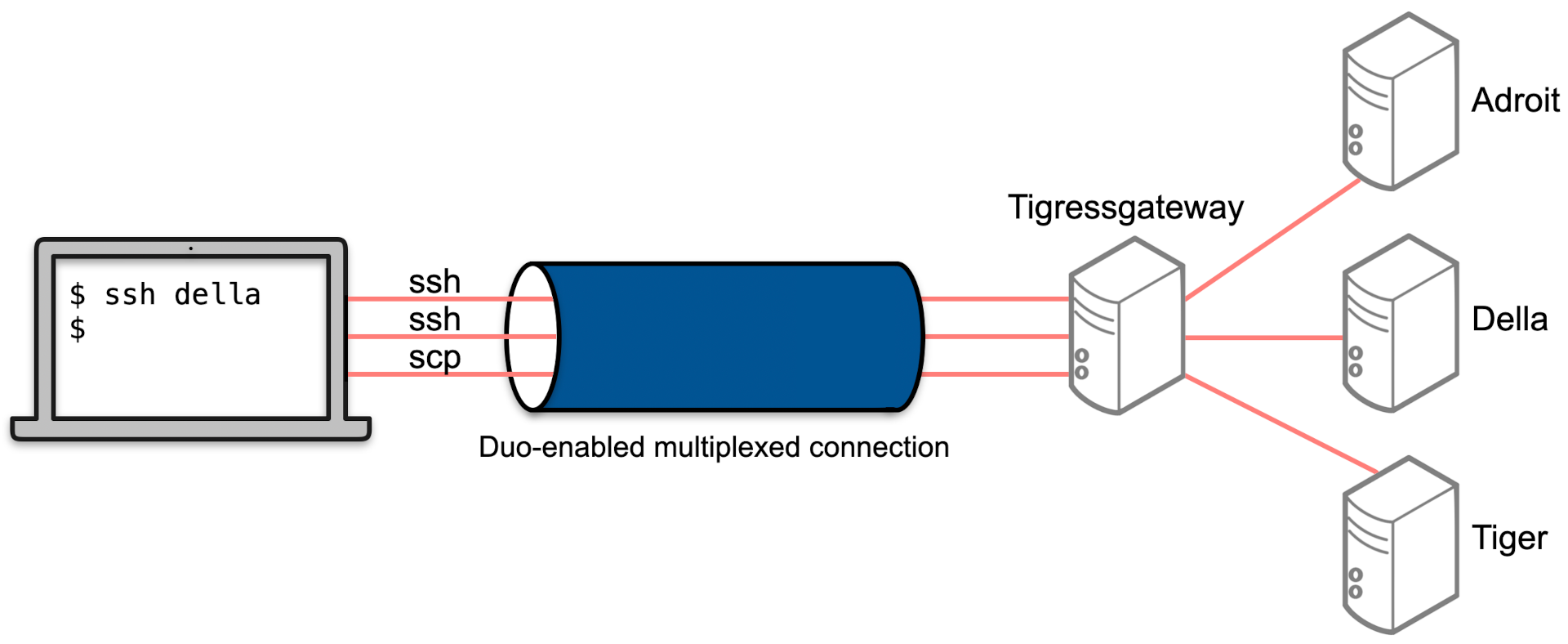
The procedure for doing this is shown below:
Step 1: On your local machine (laptop/desktop) run the command below to make two directories and set the permissions:
$ mkdir -p ~/.ssh/controlmasters && mkdir -p ~/.ssh/sockets && chmod 700 ~/.ssh/sockets
Step 2: Modify your .ssh/config file as follows (replace aturing with your NetID):
Mac, Linux and WSL
Host tigressgateway.princeton.edu tigressgateway
HostName tigressgateway.princeton.edu
User aturing
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
ServerAliveInterval 300
Host della.princeton.edu della
User aturing
HostName della.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
If the file ~/.ssh/config does not exist then make it using a text editor.
Step 3: SSH to a Login Node
You can then connect from your local machine (laptop/desktop) using the following command, for example:
$ ssh della
The command above will Duo authenticate but subsequent sessions will use that connection and not require Duo. The proxyjump server tigressgateway will be used. That is, the connection first goes to tigressgateway where it Duo authenticates before hopping to della.
If you need to forward local ports then add a LocalForward line after ServerAliveInterval for tigressgateway:
Host tigressgateway.princeton.edu tigressgateway
...
ServerAliveInterval 300
LocalForward 5901 della.princeton.edu:5901
This will enable port forwarding for the given ports in case you require VNC access or other processes to tunnel through (most users can ignore this). See the section for ProxyJump in man ssh_config for more. You should choose new ports between 5900 and 9999 but most users will not need port forwarding so you may choose to omit lines beginning with LocalForward.
After completing the steps above, you should be able to scp <localfile> della: without additional Duo authentications since the connection is established and multiplexed.
Below is a sample file for Mac and Linux of .ssh/config for multiple clusters (replace aturing with your NetID). You should only enter stanzas for the clusters and machines that you have acces to.
Host tigressgateway.princeton.edu tigressgateway
HostName tigressgateway.princeton.edu
User aturing
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
ServerAliveInterval 300
Host adroit.princeton.edu adroit
User aturing
HostName adroit.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host adroit-vis.princeton.edu adroit-vis
User aturing
HostName adroit-vis.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host della.princeton.edu della
User aturing
HostName della.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host della-gpu.princeton.edu della-gpu
User aturing
HostName della-gpu.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host della-vis1 della-vis2
User aturing
HostName %h.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host nobel.princeton.edu nobel
User aturing
HostName nobel.princeton.edu
Host stellar-amd.princeton.edu stellar-amd
User aturing
HostName stellar-amd.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host stellar-intel.princeton.edu stellar.princeton.edu stellar
User aturing
HostName stellar-intel.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host stellar-vis1.princeton.edu stellar-vis1
User aturing
HostName stellar-vis1.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host stellar-vis2.princeton.edu stellar-vis2
User aturing
HostName stellar-vis2.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host tiger.princeton.edu tiger
User aturing
HostName tiger.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
Host tiger-vis.princeton.edu tiger-vis
User aturing
HostName tiger-vis.princeton.edu
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/sockets/%p-%h-%r
On your local machine, to check if the multiplexed connection is alive (remember everything is going through tigressgateway):
$ ssh -O check tigressgateway
To end the connection manually:
$ ssh -O stop tigressgateway
On-Campus Only
Almost all users should follow the directions for On-Campus and Off-Campus above but if for some reason you only want to enable multiplexing when you are on-campus then follow this procedure.
Step 1: To make this work, on your Linux or macOS local machine (laptop/desktop), edit the file ~/.ssh/config by adding a machine stanza which looks like this (replace aturing with your NetID):
Host della.princeton.edu della
User aturing
HostName della.princeton.edu
ControlPath ~/.ssh/controlmasters/%r@%h:%p
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist 10m
Step 2: Then do a mkdir -p ~/.ssh/controlmasters to create the directory for telling ssh how to use this multiplexed session.
The very first login to della (from on-campus since no VPN) would start the multiplexing option:
$ ssh della
The command above will Duo authenticate but subsequent sessions will use that connection and not require Duo. The multiplexer remains active for ControlPersist time, as defined in your ~/.ssh/config file, once the last ssh session has terminated.
Some handy commands from your local machine (laptop/desktop):
$ ssh -O check della # this checks whether a multiplexed session is already open
$ ssh -O stop della # kills the multiplexed session
The line Host della.princeton.edu della allows one to create aliases which explains why we can use della or della.princeton.edu in the commands above.
Troubleshooting
To ignore your config file:
$ ssh -F /dev/null <YourNetID>@della.princeton.edu
To use an alternate config file:
$ ssh -F /path/to/alternate/config <hostname>
In some cases it may be necessary to close active ssh sessions on your local machine. First, find the open sessions:
$ ps uwx | grep -E 'PID|ssh'
Then kill specific processes (see the PID column to get the process id):
$ kill -9 <process-id>
X11 Forwarding with SSH Multiplexing
If you are using ssh multiplexing AND the first connection you made did not use X11 forwarding then none that follow will do so either and attempting to add -Y/-X is useless. In this case you have to close all ssh connections to the machine (ALL is very important - it has to ask you for password/username/duo again) and then reconnect making sure that the first connection uses -Y/-X flag.
X11 Forwarding
If you are on a Mac and you experience problems with X11 forwarding then try adding the following lines to the bottom of ~/.ssh/config:
Host *
ForwardAgent yes
ForwardX11 yes
XAuthLocation /opt/X11/bin/xauth
Make sure that you have an X server running (e.g., XQuartz) when using this approach. There are better approaches to working with graphics on the Research Computing clusters than X11.
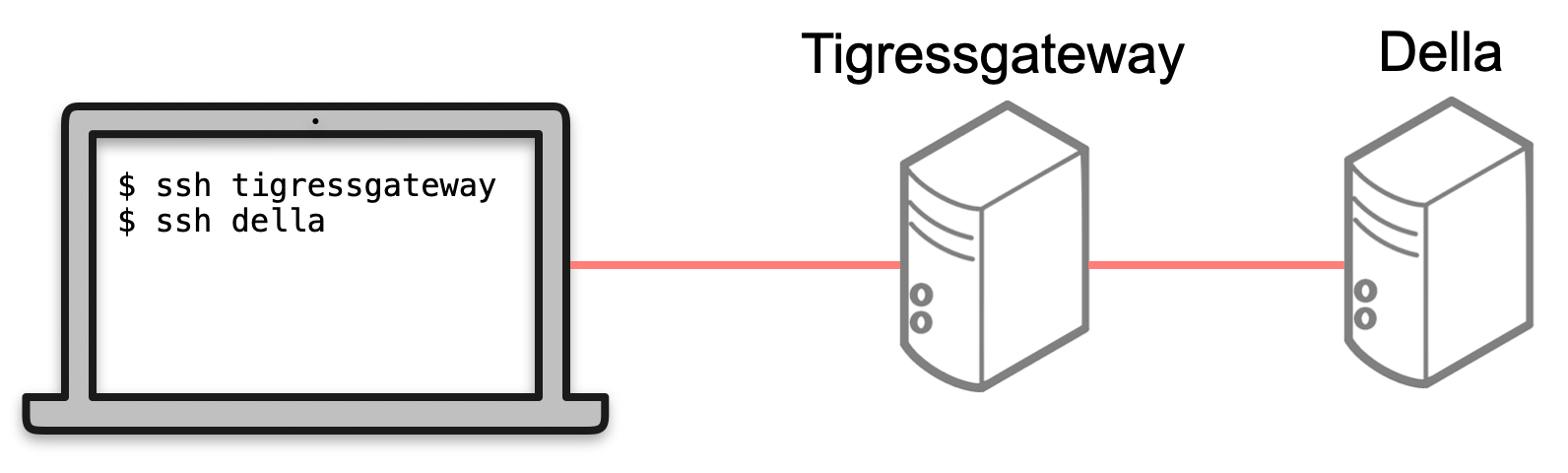
III. VPN Free (but without SSH multiplexing, large clusters only)
This approach is worth knowing about in general. Some Windows users may prefer it if using the VPN is an issue. You must have an account on one of the large clusters (e.g., Della).
The procedure is to ssh to tigressgateway.princeton.edu and then from there, ssh to your desired cluster (e.g., della) as shown in the figure below. A VPN is not required since tigressgateway is open to the world. You must have an account on one of the large clusters to do this (e.g., Della). If you are transferring many files you will want to use one of the approaches above to avoid Duo authentication.
Time Saver
You do not need to connect to tigressgateway explicitly. Instead, save time by modifying your .ssh/config file as follows (replace aturing with your NetID):
Windows
Use a text editor to add these lines to C:\Users\<username>\.ssh:
Host tigressgateway.princeton.edu tigressgateway
HostName tigressgateway.princeton.edu
User aturing
MACs hmac-sha2-512
Host della.princeton.edu della
User aturing
HostName della.princeton.edu
MACs hmac-sha2-512
ProxyJump tigressgateway.princeton.edu
Once you have this set up, you can connect to a large cluster like Della directly from your local machine without explicitly first connecting to tigressgateway:
$ ssh della
The ProxyJump setting causes tigressgateway to be used as a silent intermediary. The tigressgateway server is open to the world while the login nodes on the large clusters are not.